Symptoms & Diagnosis
Because of their location in the brainstem, DIPGs cause pressure on the cranial nerves that originate in the pons as they grow. These nerves control muscles used to move the eyes and the face and to chew and swallow. The symptoms of DIPG include double vision, difficulty in controlling eye and eyelid movement and facial expression, and difficulty chewing and swallowing. Pressure on other nerves may cause weakness in the arms and the legs and difficulty speaking and walking.
The tumor itself and a related condition called hydrocephalus (the build-up of fluid in the brain) increase pressure inside the skull, which can cause headaches (especially in the morning), nausea and vomiting, and fatigue.
Because DIPGs grow quickly, symptoms usually get worse quickly.
If your doctor suspects a brain tumor, he or she will conduct a physical examination and will order tests to collect more information. Brain tumors are usually diagnosed using imaging, including computerized tomography (also called CT or CAT scans), and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI).
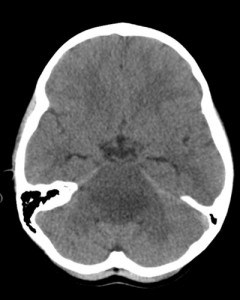
A CT scan uses x-rays to create a series of images of vertical and horizontal sections of the brain (often referred to as slices). A CT scan can show differences in density between tumor and normal brain tissue, and can also show if a tumor is compressing the surrounding brain. It is very sensitive for the detection of bleeding, and can be obtained quickly and easily.
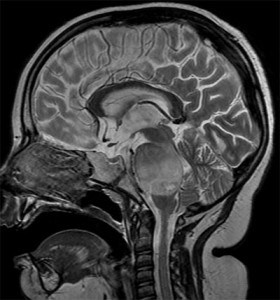
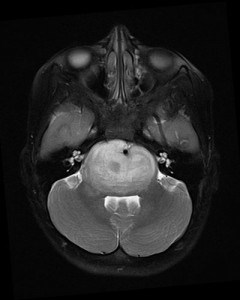
MRI uses magnetic fields and radio waves to create detailed images, and can provide incredibly detailed pictures of the brain. MRI scans can more clearly show brain tumors and how far they extend into the surrounding brain, as well as help determine the type of tumor and sometimes predict its future growth. Specialized MR techniques like MRS may give even more detailed information about tumors. MR exams typically take about an hour to complete, and young children often need to be put to sleep for the exam.
For information about the role of surgical biopsy in the diagnosis of DIPG, please see the Biopsy page.